نصب و پیکربندی سوییچ Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3120
Switch Installation
This chapter provides instructions on how to install your Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3120 for HP, also referred to as the switch module, in the HP c-Class BladeSystem enclosure and how to set up and configure your switch module. The HP c-Class BladeSystem, referred to as the blade enclosure, is a system that supports up to 16 server modules and up to 8 Ethernet switch modules. The switch module is installed in one of the enclosure I/O module bays on the rear panel of the server enclosure.
This chapter also describes how to interpret the power-on self-test (POST) that ensures proper operation and how to make connections to the switch module.
Read the topics and perform the procedures in this order:
•![]() HP c-Class BladeSystem Enclosure Architecture
HP c-Class BladeSystem Enclosure Architecture
•![]() Installing the Switch Module in the Blade Enclosure
Installing the Switch Module in the Blade Enclosure
•![]() Planning and Creating a Switch Stack
Planning and Creating a Switch Stack
•![]() Installing Devices in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet Slots
Installing Devices in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet Slots
•![]() Connecting to the 10/100/1000 Ports
Connecting to the 10/100/1000 Ports
•![]() Planning 10/100/1000 Ethernet Port Connections
Planning 10/100/1000 Ethernet Port Connections
Preparing for Installation
This section covers these topics:
Safety Warnings
These safety warnings are translated into several languages in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP that ships with the product. The EMC regulatory statements are also included in that guide.

Warning ![]() To prevent the switch from overheating, do not operate it in an area that exceeds the maximum recommended ambient temperature of 113°F (45°C). To prevent airflow restriction, allow at least 3 inches (7.6 cm) of clearance around the ventilation openings. Statement 17B
To prevent the switch from overheating, do not operate it in an area that exceeds the maximum recommended ambient temperature of 113°F (45°C). To prevent airflow restriction, allow at least 3 inches (7.6 cm) of clearance around the ventilation openings. Statement 17B

Warning ![]() Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. Statement 43
Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. Statement 43

Warning ![]() Ethernet cables must be shielded when used in a central office environment. Statement 171
Ethernet cables must be shielded when used in a central office environment. Statement 171

Warning ![]() Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. Statement 1001
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. Statement 1001

Warning ![]() Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source. Statement 1004
Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source. Statement 1004

Warning ![]() Class 1 laser product. Statement 1008
Class 1 laser product. Statement 1008

Warning ![]() Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030

Warning ![]() Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040

Warning ![]() For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection.
For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection.
10/100/1000 Ethernet Statement 1044

Warning ![]() Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Installation Guidelines
Before you install the switch module in the blade enclosure, read these guidelines:
•![]() Review and become familiar with the safety and handling guidelines specified in the blade enclosure Product Information Guide.
Review and become familiar with the safety and handling guidelines specified in the blade enclosure Product Information Guide.
•![]() Review the “Safety Warnings” section and the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP that accompanies this guide.
Review the “Safety Warnings” section and the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP that accompanies this guide.
Consider these prerequisites before installing your switch module:
•![]() Fill any empty interconnect bays or any empty power module bays in the blade enclosure with blanks.
Fill any empty interconnect bays or any empty power module bays in the blade enclosure with blanks.
•![]() Identify the bays in which you will insert the switch modules. Plan to install the first switch module in bay 1, the second in bay 2, and so on up to bay 8, if possible. The bay in which you choose to install each switch module depends on whether mezzanine or Ethernet cards are installed in the blade enclosure and how they are configured. See the blade enclosure documentation for more information about installing and configuring the mezzanine or Ethernet cards.
Identify the bays in which you will insert the switch modules. Plan to install the first switch module in bay 1, the second in bay 2, and so on up to bay 8, if possible. The bay in which you choose to install each switch module depends on whether mezzanine or Ethernet cards are installed in the blade enclosure and how they are configured. See the blade enclosure documentation for more information about installing and configuring the mezzanine or Ethernet cards.
The interconnect module bays are physically interconnected in pairs through the blade enclosure backplane. That is, each of these pairs—bays 1 and 2, bays 3 and 4, bays 5 and 6, and bays 7 and 8—are interconnected. If you install two switch modules in one of the paired bays, they are internally interconnected. You must configure the switch modules to logically enable the interconnect ports, Gigabit Ethernet ports 23 and 24. See the switch module software configuration guide for information on configuring these ports.
•![]() See the HP c-Class documentation for information on the port mapping between blade enclosures and the switch modules.
See the HP c-Class documentation for information on the port mapping between blade enclosures and the switch modules.

When you install a switch module, you do not need to power down the server modules or the enclosure.
The initial configuration assumes that the switch module was never configured, that it is in the same state as when it was received, and that it is not configured with a default username and password.
Be sure to observe these requirements:
•![]() For copper Ethernet ports, cable lengths from the switch module to connected devices can be up to 328 feet (100 meters).
For copper Ethernet ports, cable lengths from the switch module to connected devices can be up to 328 feet (100 meters).
•![]() See the documentation for the SFP module for more information about cable specifications for the SFP module connections. Also see the “SFP Module Cable Specifications” section on page B-6. Each port must match the wave-length specifications on the other end of the cable, and the cable must not exceed the stipulated cable length for reliable communications.
See the documentation for the SFP module for more information about cable specifications for the SFP module connections. Also see the “SFP Module Cable Specifications” section on page B-6. Each port must match the wave-length specifications on the other end of the cable, and the cable must not exceed the stipulated cable length for reliable communications.

Note ![]() When using shorter lengths of single-mode fiber-optic cable, you might need to insert an inline optical attenuator in the link to avoid overloading the receiver.
When using shorter lengths of single-mode fiber-optic cable, you might need to insert an inline optical attenuator in the link to avoid overloading the receiver.
•![]() Operating environment is within the ranges listed in Appendix A, “Technical Specifications.”
Operating environment is within the ranges listed in Appendix A, “Technical Specifications.”
•![]() Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise, such as radios, power lines, and fluorescent lighting fixtures. Make sure the cabling is safely away from other devices that might damage the cables.
Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise, such as radios, power lines, and fluorescent lighting fixtures. Make sure the cabling is safely away from other devices that might damage the cables.
Verifying Package Contents
Carefully remove the contents from the shipping container, and look at each item for damage. If any item is missing or damaged, contact your Cisco representative or reseller for support. Return all packing material to the shipping container, and save it.
These items ship with your switch module. The Cisco TwinGig Converter Modules with installed protective dust covers are shipped already installed on your switch module.
•![]() Console cable
Console cable
•![]() 1-meter Stackwise Plus cable
1-meter Stackwise Plus cable
•![]() Documentation CD that contains:
Documentation CD that contains:
–![]() Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP Getting Started Guide
Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP Getting Started Guide
–![]() Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP
–![]() Cisco and HP Warranty Information
Cisco and HP Warranty Information

Note ![]() If the switch modules are ordered with the blade enclosure, the switch modules are already installed, and no unpacking is required. The unpacking procedure applies only if a switch module is ordered separately.
If the switch modules are ordered with the blade enclosure, the switch modules are already installed, and no unpacking is required. The unpacking procedure applies only if a switch module is ordered separately.
HP c-Class BladeSystem Enclosure Architecture
Figure 2-1 shows the rear view of the blade enclosure in which you install the switch module.
Figure 2-1 Rear View of the Blade Enclosure
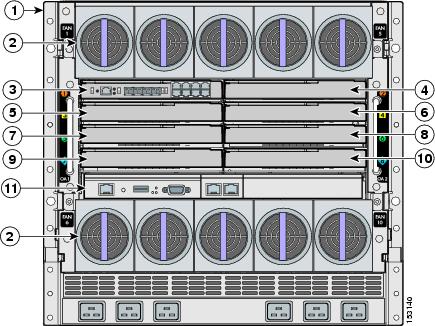
Consider these prerequisites before installing your switch module:
•![]() Plan for optimal airflow.
Plan for optimal airflow.
•![]() Fill any unoccupied server slot bays or power module bays with blanks.
Fill any unoccupied server slot bays or power module bays with blanks.
•![]() Bays 1 through 8 are available for Ethernet switch modules.
Bays 1 through 8 are available for Ethernet switch modules.
•![]() See the server enclosure documentation for information on the port mapping between blade enclosures and the switch modules.
See the server enclosure documentation for information on the port mapping between blade enclosures and the switch modules.
Installing the Switch Module in the Blade Enclosure
Before you install the switch module in the blade enclosure, consider these points:
•![]() Review and become familiar with the safety guidelines in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP that accompanies this guide.
Review and become familiar with the safety guidelines in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3000 Series for HP that accompanies this guide.
•![]() Review and become familiar with the safety guidelines in the HP BladeSystem enclosure setup and installation guide.
Review and become familiar with the safety guidelines in the HP BladeSystem enclosure setup and installation guide.
•![]() Review and become familiar with the temperature, power, and grounding requirements specified in the HP BladeSystem enclosure setup and installation guide.
Review and become familiar with the temperature, power, and grounding requirements specified in the HP BladeSystem enclosure setup and installation guide.

Warning ![]() Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030

When you install a switch module, you do not need to power down the blade enclosure.
Follow these steps to install the switch module in the blade enclosure:
Step 1 ![]() If you have not already done so, touch the static-protective package that contains the switch module to an unpainted metal part of the blade enclosure for at least 2 seconds.
If you have not already done so, touch the static-protective package that contains the switch module to an unpainted metal part of the blade enclosure for at least 2 seconds.
Step 2 ![]() Remove the switch module from its static-protective package.
Remove the switch module from its static-protective package.
Step 3 ![]() Remove the interconnect blank from the bay where you plan to install the switch module, if one is present, and install the switch module. (See Figure 2-2.)
Remove the interconnect blank from the bay where you plan to install the switch module, if one is present, and install the switch module. (See Figure 2-2.)
Figure 2-2 Removing the Interconnect Module Blank from the Blade Enclosure
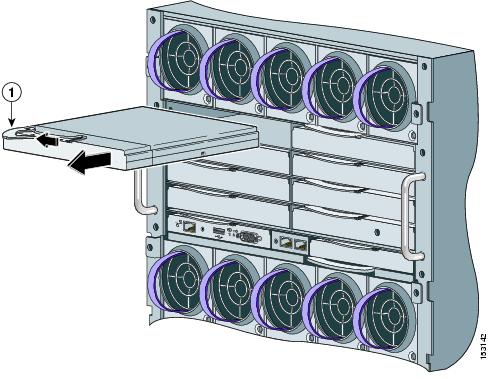
Step 4 ![]() Ensure that the release latch on the switch module is in the open position (perpendicular to the module). (See Figure 2-3.)
Ensure that the release latch on the switch module is in the open position (perpendicular to the module). (See Figure 2-3.)
Figure 2-3 Open the Release Latch
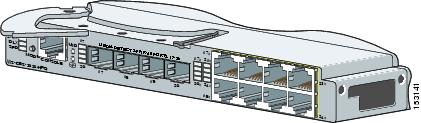
Step 5 ![]() Slide the switch module into the bay until it stops. (See Figure 2-4.)
Slide the switch module into the bay until it stops. (See Figure 2-4.)
Figure 2-4 Installing the Switch Module into the Blade Enclosure Interconnect Module Bay
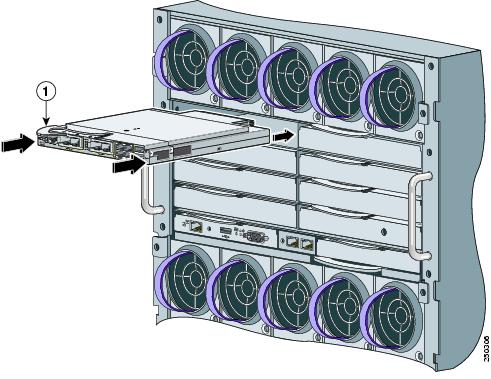
Step 6 ![]() Push the release latch on the front of the switch module to the closed position.
Push the release latch on the front of the switch module to the closed position.
Switch Module IP Addresses
IP addresses can be assigned to two of the switch module interfaces:
•![]() The Fa0 Ethernet interface. This Layer 3 Ethernet interface is connected to the Onboard Administrator through which you can manage the switch module. It is used only for switch module management traffic, not for data traffic.
The Fa0 Ethernet interface. This Layer 3 Ethernet interface is connected to the Onboard Administrator through which you can manage the switch module. It is used only for switch module management traffic, not for data traffic.
•![]() The VLAN 1 interface. You can manage the switch module from any of its external ports through VLAN 1.
The VLAN 1 interface. You can manage the switch module from any of its external ports through VLAN 1.
When you install the switch module, you need to determine whether the Onboard Administrator is connected to a network in which a DHCP server is also connected or if the Onboard Administrator has been configured as a DHCP server. If either of these conditions is true, the switch module automatically obtains an IP address for its Fa0 Ethernet interface that is connected to the Onboard Administrator. In this case, a VLAN 1 IP address is not assigned, and to set up the switch module by using the Device Manager you must use the Fa0 interface IP address that the DHCP server assigns.
See the “Using the Onboard Administrator to Assign an IP Address to the Switch Module and Running Express Setup” section for procedures on setting up the switch module if the IP address is being assigned dynamically.
Using the Onboard Administrator to Assign an IP Address to the Switch Module and Running Express Setup
Before you run Express Setup, you must set up your switch module to communicate with a hyperterminal program. The initial configuration assumes that the switch module was never configured, that it is in the same state as when it was received, and that it is not configured with a default username and password. To set up the switch module by using the command-line interface (CLI), see the switch module hardware installation guide on Cisco.com.
For the switch module to obtain an IP address for the Fa0 interface through the Onboard Administrator, these conditions must be met:
•![]() The blade enclosure is powered on and connected to the network.
The blade enclosure is powered on and connected to the network.
•![]() Basic configuration of the Onboard Administrator is completed, and you have the username and password for the Onboard Administrator.
Basic configuration of the Onboard Administrator is completed, and you have the username and password for the Onboard Administrator.
•![]() A DHCP server is configured on the network segment to which the blade enclosure is connected, or the Onboard Administrator is configured to run as a DHCP server.
A DHCP server is configured on the network segment to which the blade enclosure is connected, or the Onboard Administrator is configured to run as a DHCP server.
See the Onboard Administrator user guide at http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation for more information about configuring and using the Onboard Administrator.
After you install the switch module in the interconnect module bay, after approximately 2 minutes, the switch module automatically obtains an IP address for its Fa0 interface through the Onboard Administrator. This method of obtaining an IP address occurs if a DCHP server is configured on the same network, or if the Onboard Administrator is configured as a DHCP server.
After you have installed the switch module (see the “Installing the Switch Module in the Blade Enclosure” section), it powers on. The switch module begins the POST, a series of tests that runs automatically to ensure that the switch module functions properly.
Step 1 ![]() Wait for the switch module to complete POST. It might take several minutes for the switch module to complete POST.
Wait for the switch module to complete POST. It might take several minutes for the switch module to complete POST.
Step 2 ![]() Verify that POST has completed by confirming that the system and status LEDs remain green.
Verify that POST has completed by confirming that the system and status LEDs remain green.
If the switch module fails POST, the system LED turns amber. If the POST fails, see the “Verify the Switch Module POST Results” section on page 3-1 to determine a course of action. POST errors are usually fatal. Call Cisco Systems immediately if your switch module fails POST.
Step 3 ![]() Wait approximately 2 minutes for the switch module to get the software image from its flash memory and to begin autoinstallation.
Wait approximately 2 minutes for the switch module to get the software image from its flash memory and to begin autoinstallation.
If you already have the Onboard Administrator open through a browser window, go to Step 5.
Step 4 ![]() Using a PC that is connected to the same network segment as the blade enclosure Onboard Administrator, access the Onboard Administrator in a browser window. Enter your assigned user name and password.
Using a PC that is connected to the same network segment as the blade enclosure Onboard Administrator, access the Onboard Administrator in a browser window. Enter your assigned user name and password.
Step 5 ![]() Choose Enclosure Information > Interconnect Bays to open the Interconnect Bay Summary window where you can find the assigned IP address of the switch module Fa0 interface in the Management URL column. (See Figure 2-5.)
Choose Enclosure Information > Interconnect Bays to open the Interconnect Bay Summary window where you can find the assigned IP address of the switch module Fa0 interface in the Management URL column. (See Figure 2-5.)
Figure 2-5 Onboard Administrator Interconnect Bay Summary Window
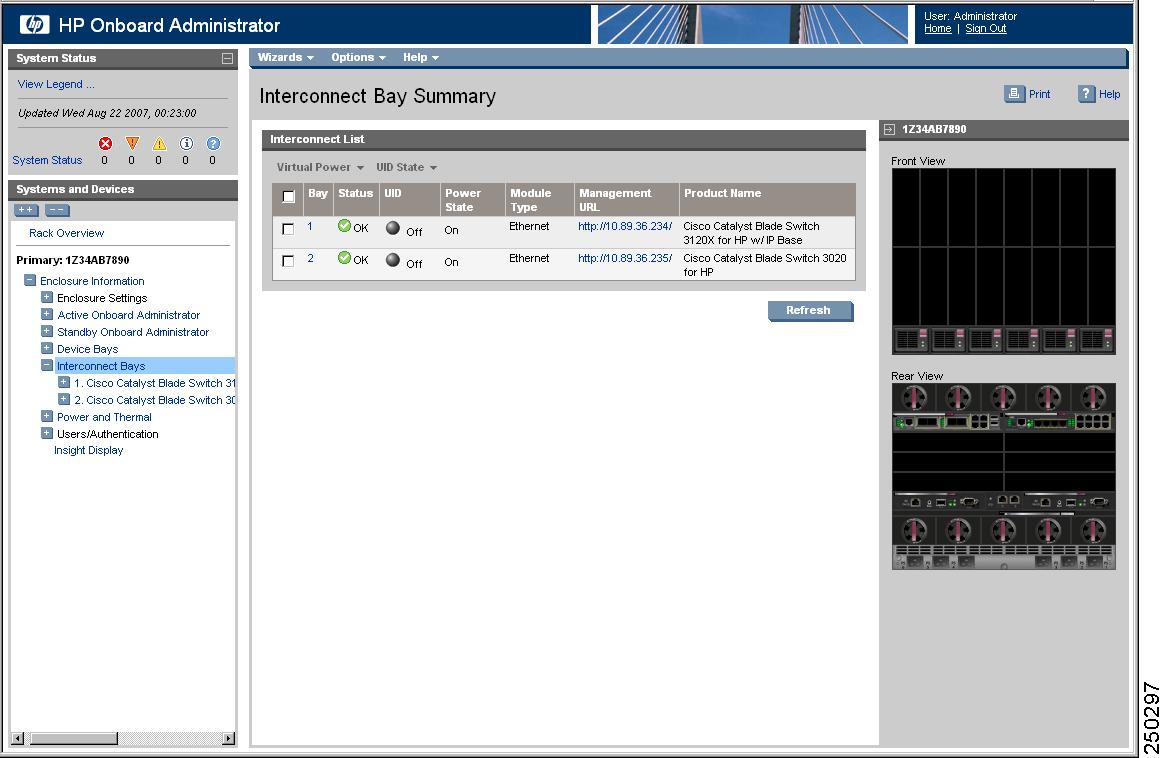
Step 6 ![]() Click the IP address hyperlink for the switch module from the Management URL column to open a new browser window.
Click the IP address hyperlink for the switch module from the Management URL column to open a new browser window.
Step 7 ![]() On the left side of the Onboard Administrator, choose Configuration > Express Setup.
On the left side of the Onboard Administrator, choose Configuration > Express Setup.
The Express Setup page appears (see Figure 2-6). (Close or minimize the Device Manager Help window.)
Figure 2-6 Express Setup Page
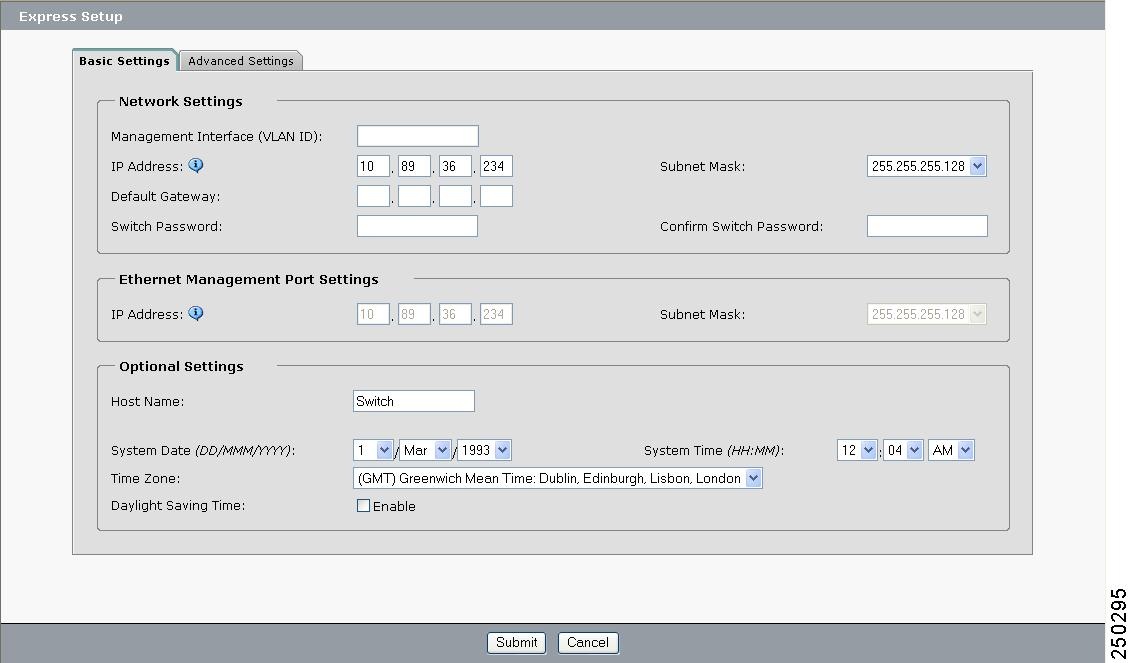
Step 8 ![]() Go to “Using Express Setup” section to finish setting up the switch module.
Go to “Using Express Setup” section to finish setting up the switch module.
Using Express Setup
Before you complete the setup program, obtain the default gateway IP address and the switch password from your system administrator. You can use Express Setup to configure these optional parameters through the Express Setup program:
•![]() Telnet access password
Telnet access password
•![]() Names of the SNMP read and write community strings if you are going to use a network-management program like CiscoWorks.
Names of the SNMP read and write community strings if you are going to use a network-management program like CiscoWorks.
•![]() Host name, system contact, and system location
Host name, system contact, and system location
•![]() System time, time zone, Daylight Savings Time enable
System time, time zone, Daylight Savings Time enable
Follow these steps to finish setting up the switch module. The Onboard Administrator assigns an IP address and a subnet mask to the management interface (VLAN ID) and to the Ethernet management port.
Step 1 ![]() Enter this information in the Network Settings fields.
Enter this information in the Network Settings fields.
•![]() In the Default Gateway field, enter the IP address for the default gateway (router).
In the Default Gateway field, enter the IP address for the default gateway (router).
•![]() In the Switch Password field, enter your password. The password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, can start with a number, is case sensitive, allows embedded spaces, but does not allow spaces at the beginning or end.
In the Switch Password field, enter your password. The password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, can start with a number, is case sensitive, allows embedded spaces, but does not allow spaces at the beginning or end.
In the Confirm Switch Password field, enter your password again.
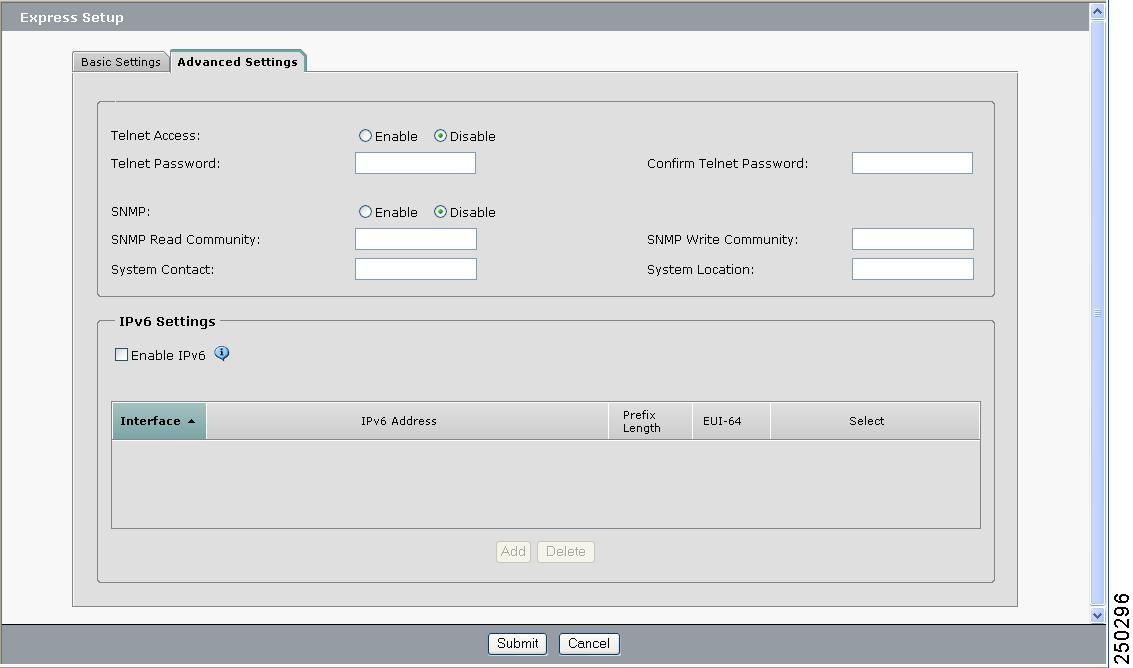
You can enter the Optional Settings information now or enter it later by using the device manager interface. Some of these settings are on the Advanced Settings tab (see Figure 2-7).
Figure 2-7 Express Setup Advanced Settings Table
Step 2 ![]() In the Host Name field, enter a name for the switch module. The host name is limited to 31 characters; embedded spaces are not allowed.
In the Host Name field, enter a name for the switch module. The host name is limited to 31 characters; embedded spaces are not allowed.
Step 3 ![]() In the System Date and System Time fields, enter the current date and time, or use the down arrows to select them.
In the System Date and System Time fields, enter the current date and time, or use the down arrows to select them.
Step 4 ![]() In the Time Zone field, use the down arrow to choose your time zone.
In the Time Zone field, use the down arrow to choose your time zone.
Step 5 ![]() Click Enable in the Daylight Savings Time field to enable this feature.
Click Enable in the Daylight Savings Time field to enable this feature.
Step 6 ![]() In the Telnet Access field, click Enable if you are going to use Telnet to manage the switch module by using the CLI. If you enable Telnet access, you must enter a Telnet password.
In the Telnet Access field, click Enable if you are going to use Telnet to manage the switch module by using the CLI. If you enable Telnet access, you must enter a Telnet password.

Note ![]() If you plan to create a switch stack, enable Telnet access so that you can use the CLI to set this switch to the highest priority. See the “Planning and Creating a Switch Stack” section for more information about creating a switch stack.
If you plan to create a switch stack, enable Telnet access so that you can use the CLI to set this switch to the highest priority. See the “Planning and Creating a Switch Stack” section for more information about creating a switch stack.
Step 7 ![]() In the Telnet Password field, enter a password. The Telnet password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, is case sensitive, allows embedded spaces, but does not allow spaces at the beginning or end. In the Confirm Telnet Password field, re-enter the Telnet password.
In the Telnet Password field, enter a password. The Telnet password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, is case sensitive, allows embedded spaces, but does not allow spaces at the beginning or end. In the Confirm Telnet Password field, re-enter the Telnet password.
Step 8 ![]() In the SNMP field, click Enable to enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Enable SNMP only if you plan to manage switches by using CiscoWorks 2000 or another SNMP-based network-management system.
In the SNMP field, click Enable to enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Enable SNMP only if you plan to manage switches by using CiscoWorks 2000 or another SNMP-based network-management system.
Step 9 ![]() If you enable SNMP, you must enter a community string in the SNMP Read Community field, the SNMP Write Community field, or both. SNMP community strings authenticate access to MIB objects. Embedded spaces are not allowed in SNMP community strings. When you set the SNMP read community, you can access SNMP information, but you cannot modify it. When you set the SNMP write community, you can both access and modify SNMP information.
If you enable SNMP, you must enter a community string in the SNMP Read Community field, the SNMP Write Community field, or both. SNMP community strings authenticate access to MIB objects. Embedded spaces are not allowed in SNMP community strings. When you set the SNMP read community, you can access SNMP information, but you cannot modify it. When you set the SNMP write community, you can both access and modify SNMP information.
Step 10 ![]() In the System Contact field, enter the name of the person who is responsible for the switch module. In the System Location field, enter the wiring closet, floor, or building where the switch module is located.
In the System Contact field, enter the name of the person who is responsible for the switch module. In the System Location field, enter the wiring closet, floor, or building where the switch module is located.
Step 11 ![]() Click Submit to save your settings, or click Cancel to clear your settings.
Click Submit to save your settings, or click Cancel to clear your settings.
You can close this window.
To install additional switch modules, repeat the steps in the “Installing the Switch Module in the Blade Enclosure” section through the “Using the Onboard Administrator to Assign an IP Address to the Switch Module and Running Express Setup” section.
Setting the Installed Switch Module As the Stack Master
If you plan to create a switch stack, we recommend that you set the switch module that you first configured as the stack master. To do this, you must assign the highest priority value to this switch module. To assign a priority value after you have installed and initially configured the first switch module, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Launch a Telnet session by connecting directly to the switch through its console port, or by using the Onboard Administrator:
Launch a Telnet session by connecting directly to the switch through its console port, or by using the Onboard Administrator:
On the left side of the Onboard Administrator, click + next to Interconnect Bays to expand it, then click + next to the name of the switch you want to set as the switch master. Click Management Console to open the device manager for the switch, and if prompted, enter the user name and password for the switch. Under Contents, choose Maintenance > Telnet.
Step 2 ![]() Enter enable.
Enter enable.
Step 3 ![]() Enter configure terminal.
Enter configure terminal.
Step 4 ![]() Enter switch 1 priority 15.
Enter switch 1 priority 15.
Step 5 ![]() At the prompt, press Return.
At the prompt, press Return.
Step 6 ![]() Enter end.
Enter end.
Step 7 ![]() Enter copy running-configuration startup-configuration to save this setting.
Enter copy running-configuration startup-configuration to save this setting.
Step 8 ![]() At the prompt, press Return.
At the prompt, press Return.
Step 9 ![]() To verify that this switch is set as the switch master, enter the show switch user EXEC command.
To verify that this switch is set as the switch master, enter the show switch user EXEC command.
For more information about creating switch stacks, see the “Planning and Creating a Switch Stack” section.
Refreshing the PC IP Address
After you complete Express Setup, you should refresh the PC IP address:
•![]() For a dynamically assigned IP address, disconnect the PC from the switch module, and reconnect the PC to the network. The network DHCP server assigns a new IP address to the PC.
For a dynamically assigned IP address, disconnect the PC from the switch module, and reconnect the PC to the network. The network DHCP server assigns a new IP address to the PC.
•![]() For a statically assigned IP address, change it to the previously configured IP address.
For a statically assigned IP address, change it to the previously configured IP address.
Planning and Creating a Switch Stack
A switch stack is a set of up to nine stacking-capable switch modules that are connected through their StackWise Plus ports. One of the switches controls the operation of the stack and is called the stack master. The stack master and the other switches in the stack are stack members. Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols present the entire switch stack as a single entity to the network. Stacking is optional.
When switch modules are not stacked, each acts as a standalone switch. For general concepts and procedures to manage switch stacks, see the switch module software configuration guide and command reference on Cisco.com.

Before you connect the switch modules in a stack, keep in mind these stacking guidelines:
•![]() You should install the stack master switch module and run the initial setup program on that switch module before you connect the StackWise Plus cables to other stack members. We recommend that you assign the highest priority value to the switch module that you prefer to be the stack master. This ensures that the switch is re-elected as stack master if a re-election occurs. As you add new switch modules to the stack, they automatically become stack members.
You should install the stack master switch module and run the initial setup program on that switch module before you connect the StackWise Plus cables to other stack members. We recommend that you assign the highest priority value to the switch module that you prefer to be the stack master. This ensures that the switch is re-elected as stack master if a re-election occurs. As you add new switch modules to the stack, they automatically become stack members.
To assign a priority value through the Onboard Administrator after you have installed and initially configured the first switch module, see the “Setting the Installed Switch Module As the Stack Master” section.
•![]() When you connect the StackWise Plus cables and create a stack, you can communicate with the master switch internal Ethernet management port (Fa0) port, but not the Fa0 ports of the member switches. Only one Fa0 interface can be active, and that interface is the one on the active stack master.
When you connect the StackWise Plus cables and create a stack, you can communicate with the master switch internal Ethernet management port (Fa0) port, but not the Fa0 ports of the member switches. Only one Fa0 interface can be active, and that interface is the one on the active stack master.
•![]() For conditions that might cause a stack master re-election or to manually elect the stack master, see the “Managing Switch Stacks” chapter in the switch module software configuration guide on Cisco.com.
For conditions that might cause a stack master re-election or to manually elect the stack master, see the “Managing Switch Stacks” chapter in the switch module software configuration guide on Cisco.com.
•![]() You can stack any combination of up to nine Catalyst 3120G and 3120X switches. You can stack only the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3120 for HP switch modules; other switches are not supported.
You can stack any combination of up to nine Catalyst 3120G and 3120X switches. You can stack only the Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3120 for HP switch modules; other switches are not supported.
•![]() Before installation, verify the StackWise Plus cable length. Depending on your configuration, you might need different sized cables. The 1-meter cable is suppled if you do not specify the length of the StackWise Plus cable when you order your product. If you need the 0.5-meter cable or the 3-meter cable, you can order these StackWise Plus cables from your Cisco sales representative:
Before installation, verify the StackWise Plus cable length. Depending on your configuration, you might need different sized cables. The 1-meter cable is suppled if you do not specify the length of the StackWise Plus cable when you order your product. If you need the 0.5-meter cable or the 3-meter cable, you can order these StackWise Plus cables from your Cisco sales representative:
–![]() CAB-STK-E-0.5M= (0.5-meter cable)
CAB-STK-E-0.5M= (0.5-meter cable)
–![]() CAB-STK-E-1M= (1-meter cable)
CAB-STK-E-1M= (1-meter cable)
–![]() CAB-STK-E-3M= (3-meter cable)
CAB-STK-E-3M= (3-meter cable)
For switch module dimensions, StackWise Plus cable part numbers, and additional stacking guidelines, see the switch module hardware installation guide on Cisco.com. For concepts and procedures to manage switch stacks, see the switch module software configuration guide and the stack compatibility guide also on Cisco.com.
To create a switch stack:
•![]() Install the member switch modules if you have not already done so.
Install the member switch modules if you have not already done so.
•![]() Connect the StackWise Plus cables as described in the “Planning and Creating a Switch Stack” section.
Connect the StackWise Plus cables as described in the “Planning and Creating a Switch Stack” section.
•![]() Configure the member switch modules through the master switch by using the CLI.
Configure the member switch modules through the master switch by using the CLI.
Stack Cabling Configurations
This section describes the recommended configurations for stacking the switches by using the supplied 1-meter StackWise Plus cable.
Figure 2-8 is an example of a recommended configuration in which two switch modules create a switch stack in a single blade enclosure.
Figure 2-8 Stacking Two Switch Modules in a Single Blade Enclosure to Create One Stack
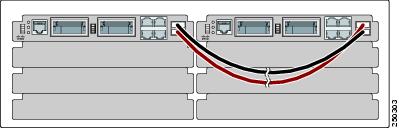
Figure 2-9 is an example of a recommended configuration in which eight switch modules create a switch stack in four blade enclosures.
Figure 2-9 Stacking Eight Switch Modules in Four Blade Enclosures to Create One Stack
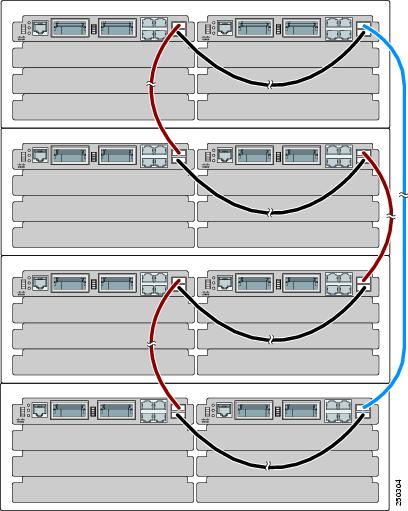
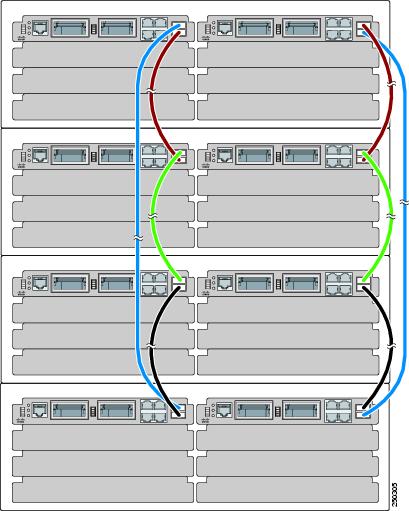
Figure 2-10 is an example of a recommended configuration in which eight switch modules create two separate switch stacks in four blade enclosures. This configuration provides redundant connections.
Figure 2-10 Stacking up to Eight Switch Modules in Four Blade Enclosures to Create Two Stacks
Connecting to the StackWise Plus Ports
Before you connect the StackWise Plus cables, review the “Planning and Creating a Switch Stack” section. Always use a Cisco-approved StackWise Plus cable to connect the switches.
Follow these steps to connect the StackWise Plus cable to the StackWise Plus ports:
Step 1 ![]() Remove the dust covers from the StackWise Plus cables and StackWise Plus ports, and store them for future use.
Remove the dust covers from the StackWise Plus cables and StackWise Plus ports, and store them for future use.
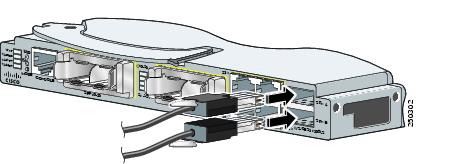
Step 2 ![]() Use the window in the StackWise Plus cable to align the connector correctly. Insert the cable into the StackWise Plus port on the front of the switch module (Figure 2-11). Use a ratcheting torque screwdriver to tighten the retainer screws to 5 lbf-in. (80 ozf-in.).
Use the window in the StackWise Plus cable to align the connector correctly. Insert the cable into the StackWise Plus port on the front of the switch module (Figure 2-11). Use a ratcheting torque screwdriver to tighten the retainer screws to 5 lbf-in. (80 ozf-in.).
Step 3 ![]() Insert the other end of the cable into the connector of the other switch module, and tighten the retainer screws to 5 lbf-in. (80 ozf-in.). Be careful not to overtighten the screws.
Insert the other end of the cable into the connector of the other switch module, and tighten the retainer screws to 5 lbf-in. (80 ozf-in.). Be careful not to overtighten the screws.
Figure 2-11 Inserting the StackWise Plus Cable in a StackWise Plus Port

Caution ![]() Removing and installing the StackWise Plus cable can shorten its useful life. Do not remove and insert the cable more often than is absolutely necessary.
Removing and installing the StackWise Plus cable can shorten its useful life. Do not remove and insert the cable more often than is absolutely necessary.
When you need to remove the StackWise Plus cable from the connector, make sure to fully unscrew the correct screws before removing the connector. When the connectors are not being used, replace the dust covers to protect them from dust.
Installing Devices in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet Slots
These sections describe how to install and remove X2 transceiver modules, Cisco TwinGig Converter Modules (also known as converter modules), and SFP modules:
•![]() Installing X2 Transceiver Modules and Cisco Converter Modules
Installing X2 Transceiver Modules and Cisco Converter Modules




Installing X2 Transceiver Modules and Cisco Converter Modules
These sections describe how to install and remove X2 transceiver modules and the converter modules in the switch module 10-Gigabit Ethernet module slots.

Note ![]() Do not remove the dust cover from the converter module until you are ready to install an X2 transceiver or SFP modules. A module or dust cover must be installed in the slot at all times.
Do not remove the dust cover from the converter module until you are ready to install an X2 transceiver or SFP modules. A module or dust cover must be installed in the slot at all times.
Use only Cisco X2 transceiver modules and Cisco TwinGig Converter Modules with the switch module. Each Cisco transceiver and converter module has an internal serial EEPROM that is encoded with security information. This encoding provides a way for Cisco to identify and validate that the module meets the requirements for the switch.
For more information about installing, removing, cabling, and troubleshooting X2 transceiver modules, see the module documentation that shipped with your device. For module cable specifications, see Appendix B, “Connector and Cable Specifications.”
Installing a Transceiver or Converter Module
When you install or remove the converter module, the mode on the switch changes from 10-Gigabit Ethernet to Gigabit Ethernet or the reverse. During this mode change, data traffic on the other switch module uplink ports (X2 transceiver or SFP module ports) might temporarily stop. When you install or remove an X2 transceiver or SFP module, traffic delay does not occur.
To insert an X2 transceiver module or a converter module, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Step 2 ![]() Remove the transceiver or converter module from its protective packaging.
Remove the transceiver or converter module from its protective packaging.
Step 3 ![]() Align the transceiver module in the module slot (Figure 2-12 and Figure 2-13).
Align the transceiver module in the module slot (Figure 2-12 and Figure 2-13).

Step 4 ![]() Slide the transceiver or converter module into the opening until the back of its faceplate is flush with the switch module faceplate.
Slide the transceiver or converter module into the opening until the back of its faceplate is flush with the switch module faceplate.
Figure 2-12 Installing X2 Transceiver Modules
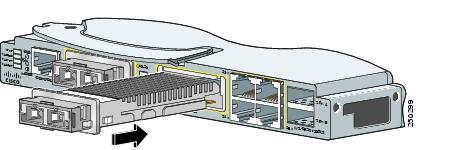

Figure 2-13 Installing Converter Modules
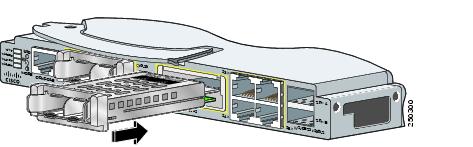
Removing a Module
To remove an X2 transceiver module or a converter module, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Step 2 ![]() For X2 transceiver modules, disconnect the cables from the module. For fiber-optic modules, install the optical bore dust plugs.
For X2 transceiver modules, disconnect the cables from the module. For fiber-optic modules, install the optical bore dust plugs.
Step 3 ![]() For converter modules, disconnect the cables from the SFP module. Remove the SFP modules from the converter module.
For converter modules, disconnect the cables from the SFP module. Remove the SFP modules from the converter module.

Step 4 ![]() Carefully pull on the X2 module sleeve, or pinch the tabs on the converter module to disengage it from the slot. Grasp the edges of the module, and carefully slide it out of the slot.
Carefully pull on the X2 module sleeve, or pinch the tabs on the converter module to disengage it from the slot. Grasp the edges of the module, and carefully slide it out of the slot.
Step 5 ![]() Reinstall the dust cover in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet slot.
Reinstall the dust cover in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet slot.

Step 6 ![]() Place the module in an antistatic bag or other protective environment.
Place the module in an antistatic bag or other protective environment.
Installing SFP Modules
This section describes how to install and remove SFP modules in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet slots. To use SFP modules in the switch, you must have a converter module installed in a 10-Gigabit Ethernet slot.

See the switch module release notes on Cisco.com for the list of SFP modules that the switch module supports. Use only Cisco SFP modules on the switch. Each Cisco module has an internal serial EEPROM that is encoded with security information. This encoding provides a way for Cisco to identify and validate that the SFP module meets the requirements for the switch.
For more information about installing, removing, cabling, and troubleshooting SFP modules, see the module documentation that shipped with your device. For module cable specifications, see Appendix B, “Connector and Cable Specifications.”
Installing an SFP Module
To insert an SFP module into a converter module slot, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Step 2 ![]() Remove the Cisco TwinGig Converter Module dust cover and save.
Remove the Cisco TwinGig Converter Module dust cover and save.

Note ![]() The dust cover is an integral part of the airflow function. If you remove the SFP module, you must replace it with the saved dust cover.
The dust cover is an integral part of the airflow function. If you remove the SFP module, you must replace it with the saved dust cover.
Step 3 ![]() Install the converter module in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet module slot as described in “Installing a Transceiver or Converter Module” section.
Install the converter module in the 10-Gigabit Ethernet module slot as described in “Installing a Transceiver or Converter Module” section.
Step 4 ![]() Find the send (TX) and receive (RX) markings that identify the top side of the SFP module.
Find the send (TX) and receive (RX) markings that identify the top side of the SFP module.
On some SFP modules, the send and receive (TX and RX) markings might be replaced by arrows that show the direction of the connection, either send or receive (TX or RX).
Step 5 ![]() If the SFP module has a bale-clasp latch, move it to the open, unlocked position.
If the SFP module has a bale-clasp latch, move it to the open, unlocked position.
Step 6 ![]() Align the SFP module in the converter module opening. When installing a module in the upper module slot (slot 1), position the SFP module face up. When using the lower module slot (slot 2), position the SFP module face down.
Align the SFP module in the converter module opening. When installing a module in the upper module slot (slot 1), position the SFP module face up. When using the lower module slot (slot 2), position the SFP module face down.
Step 7 ![]() Slide the SFP module into the opening until you feel the connector on the module snap into place (Figure 2-14).
Slide the SFP module into the opening until you feel the connector on the module snap into place (Figure 2-14).
Step 8 ![]() If the module has a bale-clasp latch, close it to lock the SFP module in place.
If the module has a bale-clasp latch, close it to lock the SFP module in place.
Step 9 ![]() Remove the SFP dust plugs and save. Install the SFP cables.
Remove the SFP dust plugs and save. Install the SFP cables.
Figure 2-14 Converter Module with SFP Modules Installed
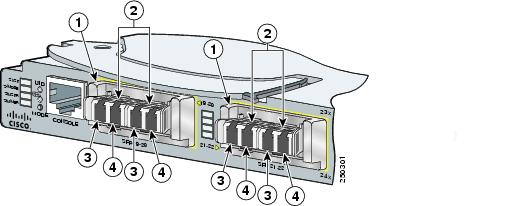
|
1
|
Converter modules |
3
|
Send (TX) optical bore |
|
2
|
SFP modules1 |
4
|
Receive (RX) optical bore |
|
1 Lower SFP modules are inverted. |
Removing an SFP Module
To remove an SFP module from a module slot, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
Step 2 ![]() Disconnect the cable from the SFP module. For reattachment, note which cable connector plug is send (TX) and which is receive (RX).
Disconnect the cable from the SFP module. For reattachment, note which cable connector plug is send (TX) and which is receive (RX).
Step 3 ![]() Insert a dust plug into the optical ports of the SFP module to keep the optical interfaces clean.
Insert a dust plug into the optical ports of the SFP module to keep the optical interfaces clean.
Step 4 ![]() If the module has a bale-clasp latch, pull the bale out and down to eject the module. If the bale-clasp latch is obstructed and you cannot use your index finger to open it, use a small, flat-blade screwdriver or other long, narrow instrument to open the bale-clasp latch.
If the module has a bale-clasp latch, pull the bale out and down to eject the module. If the bale-clasp latch is obstructed and you cannot use your index finger to open it, use a small, flat-blade screwdriver or other long, narrow instrument to open the bale-clasp latch.
Step 5 ![]() Grasp the SFP module, and carefully remove it from the module slot.
Grasp the SFP module, and carefully remove it from the module slot.
Step 6 ![]() Place the removed SFP module in an antistatic bag or other protective environment.
Place the removed SFP module in an antistatic bag or other protective environment.
Connecting to the 10/100/1000 Ports
The switch module 10/100/1000 ports configure themselves to operate at the speed of attached devices. If the attached ports do not support autonegotiation, you can explicitly set the speed and duplex parameters. Connecting devices that do not autonegotiate or that have their speed and duplex parameters manually set can reduce performance or result in no linkage.
To maximize performance, choose one of these methods for configuring the Ethernet ports:
•![]() Let the ports autonegotiate both speed and duplex.
Let the ports autonegotiate both speed and duplex.
•![]() Set the port speed and duplex parameters on both ends of the connection.
Set the port speed and duplex parameters on both ends of the connection.
Follow these steps to connect to 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX or 1000BASE-T devices:

Step 1 ![]() When connecting to workstations, servers, routers, and Cisco IP Phones, connect a straight-through cable to an RJ-45 connector on the front panel. (See Figure 2-15.) When connecting to switches or repeaters, use a crossover cable. (See the “Cable and Adapter Specifications” section on page B-4 for cable-pinout descriptions.)
When connecting to workstations, servers, routers, and Cisco IP Phones, connect a straight-through cable to an RJ-45 connector on the front panel. (See Figure 2-15.) When connecting to switches or repeaters, use a crossover cable. (See the “Cable and Adapter Specifications” section on page B-4 for cable-pinout descriptions.)
Figure 2-15 Connecting to an Ethernet Port
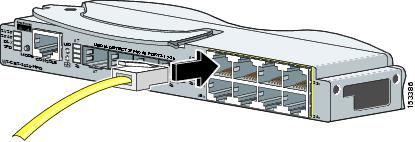

Note ![]() When connecting to 1000BASE-T-compatible devices, be sure to use a twisted four-pair, Category 5 cable.
When connecting to 1000BASE-T-compatible devices, be sure to use a twisted four-pair, Category 5 cable.

Note ![]() You can use the mdix auto interface configuration command in the CLI to enable the automatic medium-dependent interface crossover (auto-MDIX) feature. When the auto-MDIX feature is enabled, the switch module detects the required cable type for copper Ethernet connections and configures the interfaces accordingly. Therefore, you can use either a crossover or a straight-through cable for connections to a copper 10/100/1000 module port on the switch module, regardless of the type of device on the other end of the connection.
You can use the mdix auto interface configuration command in the CLI to enable the automatic medium-dependent interface crossover (auto-MDIX) feature. When the auto-MDIX feature is enabled, the switch module detects the required cable type for copper Ethernet connections and configures the interfaces accordingly. Therefore, you can use either a crossover or a straight-through cable for connections to a copper 10/100/1000 module port on the switch module, regardless of the type of device on the other end of the connection.
The auto-MDIX feature is enabled by default.
Step 2 ![]() Connect the other end of the cable to an RJ-45 connector on the other device. The port LED turns on when both the switch module and the connected device have established link.
Connect the other end of the cable to an RJ-45 connector on the other device. The port LED turns on when both the switch module and the connected device have established link.
The port LED is amber while Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) discovers the topology and searches for loops. This takes about 30 seconds, and then the port LED turns green. If the port LED does not turn on, the device at the other end might not be turned on, or there might be a cable problem or a problem with the adapter installed in the attached device. See Chapter 3, “Troubleshooting,” for solutions to cabling problems.
Step 3 ![]() Reconfigure and reboot the connected device if necessary.
Reconfigure and reboot the connected device if necessary.
Step 4 ![]() Repeat Steps 1 through 3 to connect each device.
Repeat Steps 1 through 3 to connect each device.
Planning 10/100/1000 Ethernet Port Connections
The 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports use standard RJ-45 connectors with Ethernet pinouts. The maximum cable length is 328 feet (100 meters). The 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T traffic requires Category 5, Category 5e, or Category 6 UTP cable. The 10BASE-T traffic can use Category 3 or Category 4 cable.
The autonegotiation feature is enabled by default on the switch. At this setting, the switch ports configure themselves to operate at the speed of attached device. If the attached device does not support autonegotiation, you can explicitly set the switch port speed and duplex parameters. To maximize performance, either let the ports autonegotiate both speed and duplex, or set the port speed and duplex parameters on both ends of the connection.
For simplified cabling, the automatic medium-dependent interface crossover (auto-MDIX) feature is enabled by default on the switch. With auto-MDIX enabled, the switch detects the required cable type for copper Ethernet connections and configures the interface accordingly. Therefore, you can use either a crossover or a straight-through cable for connections to a switch 10/100/1000 Ethernet port regardless of the type of device on the other end of the connection.
See the switch software configuration guide or the switch command reference on Cisco.com for more information about enabling or disabling autonegotiation and auto-MDIX.
If auto-MDIX is disabled, use the guidelines in Table 2-1 to select the correct cable for connecting the switch 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports to other devices. See the “Cable and Adapter Specifications” section on page B-4 for cable-pinout descriptions.
|
Device
|
Crossover Cable 1
|
Straight-Through Cable 1
|
|---|---|---|
|
Switch to switch |
Yes |
No |
|
Switch to hub |
Yes |
No |
|
Switch to computer or server |
No |
Yes |
|
Switch to router |
No |
Yes |
|
Switch to IP phone |
No |
Yes |
|
1 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T traffic requires twisted four-pair, Category 5, Category 5e, or Category 6 cable. 10BASE-T traffic can use Category 3 or Category 4 cable. |
Where to Go Next
If the default configuration is satisfactory, the switch module does not need further configuration. You can use any of these management options to change the default configuration:
•![]() Using the Device Manager
Using the Device Manager
Access the device manager through a web browser from anywhere in your network. Follow these steps:
a. ![]() Launch a web browser on your PC or workstation.
Launch a web browser on your PC or workstation.
b. ![]() Enter the switch module IP address in the web browser, and press Enter. The device manager page appears.
Enter the switch module IP address in the web browser, and press Enter. The device manager page appears.
c. ![]() Use the device manager to perform basic switch module configuration and monitoring. Refer to the device manager online help for more information.
Use the device manager to perform basic switch module configuration and monitoring. Refer to the device manager online help for more information.
•![]() Using the CLI
Using the CLI
The switch module CLI is based on Cisco IOS software and enhanced to support desktop-switching features. You can fully configure and monitor the switch module from the CLI. You can access the CLI either by connecting your management station directly to the switch module console port or by using Telnet from a remote management station. Refer to the switch module command reference on Cisco.com for more information.
•![]() Using SNMP
Using SNMP
You can use SNMP management applications such as CiscoWorks Small Network Management Solution (SNMS) to configure and manage the switch module. You also can manage it from an SNMP-compatible workstation that is running platforms such as HP OpenView or SunNet Manager.